SLED Cooperative Purchasing Market Landscape
Introduction to Cooperative Purchasing
Cooperative purchasing is a revolutionary approach in the State, Local, and Education (SLED) government marketplace, offering efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. This method pools the collective purchasing power of governments, enabling access to pre-negotiated contracts and bypassing lengthy RFP processes. It is especially impactful in a market exceeding $1.5 trillion annually, with 400,000 to 500,000 competitive opportunities available each year.
- Key Statistics:
- SLED market size: $1.5 trillion annually.
- Number of competitive opportunities: 400,000 to 500,000 annually.
The six levels of government engaged in cooperative purchasing include State, City, County, Special District, Independent K-12 School Districts, and Public Colleges & Universities. Each level brings unique needs, from infrastructure development to academic and research support, and benefits significantly from the flexibility and efficiency of cooperative contracts.
Overview of Cooperative Purchasing
Cooperative purchasing offers unparalleled efficiency by consolidating procurement processes into a streamlined system. Governments benefit from reduced administrative burden, quicker access to goods, and significant cost savings through bulk purchasing agreements.
- The Cooperative Process:
- Step 1: Cooperative issues a Request for Proposals (RFP).
- Step 2: Vendors submit competitive bids.
- Step 3: Contracts are awarded after evaluation.
- Step 4: Contracts are made accessible to cooperative members.
- Step 5: Members directly purchase goods and services from the cooperative catalog.
- Membership Data:
- Membership may vary based on geographic location or entity type.
- Cooperatives ensure eligibility aligns with their operational scope.
Top Cooperatives
Several leading cooperatives dominate the SLED marketplace, providing a wide array of goods and services. These include:
- BuyBoard:
- Broad product catalog.
- Caters to municipalities and schools.
- Choice Partners:
- Specializes in public sector and education contracts.
- Vendor diversity ensures robust solutions.
- GoodBuy:
- Focused on educational commodities.
- Streamlined processes for K-12 institutions.
- NASPO-ValuePoint:
- Large-scale contracts for state-level buyers.
- Delivers standardized solutions for broad needs.
- OMNIA Partners:
- Bridges public and private sector requirements.
- Provides strategic procurement solutions.
- Sourcewell:
- Innovative procurement strategies.
- Adaptable to various government levels.
Industry Profiles
Cooperative purchasing spans numerous industries, each exhibiting unique propensities for engagement. Education, healthcare, technology, and maintenance services are among the most prominent sectors.
- Education Products & Services:
- Propensity to use cooperatives: 2.79 times higher than average.
- Common purchases: Textbooks, classroom furniture, software.
- Healthcare:
- Propensity to use cooperatives: 3.16 times higher than average.
- Common purchases: PPE, medical devices, vaccines.
- Technology & Telecommunications:
- Propensity to use cooperatives: 3.31 times higher than average.
- Common purchases: Cloud services, cybersecurity, telecom hardware.
- Operations & Maintenance:
- Share of cooperative contracts: 22.4%.
- Includes: Janitorial services, waste management, facility upkeep.
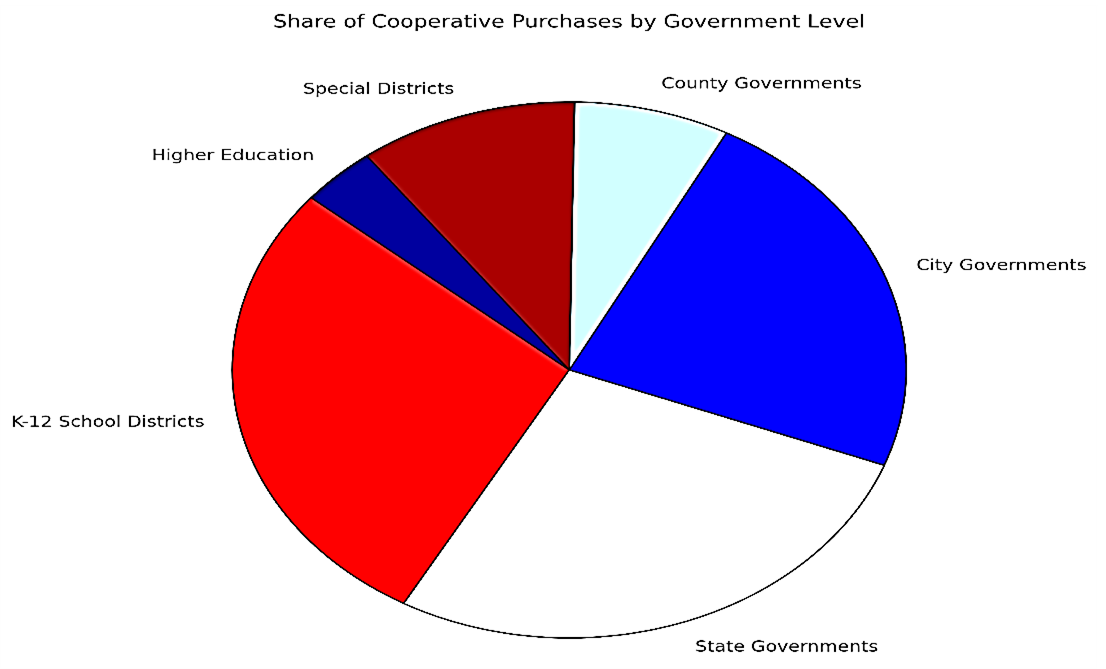
Each government level brings distinct priorities to cooperative purchasing:
Government level |
Share |
|
K-12 School Districts Focus: Classroom materials, student laptops, standardized goods |
24.7% |
|
State Governments Priorities: Healthcare and statewide technology upgrades. |
24.2% |
|
City Governments Focus: Urban transportation, public safety equipment. |
20.4% |
|
County Governments Investments: Road maintenance, vehicle fleets. |
6.6% |
|
Special Districts Specialized areas: Library systems, water treatment facilities. |
9.3% |
|
Higher Education Focus: Research equipment, campus healthcare services. |
3.2% |
Popular Products and Services in Cooperative Contracts
Cooperative contracts cater to various product and service categories:
- Medical Supplies:
- Examples: Vaccines, diagnostic kits, PPE.
- Applications: Critical for public health departments.
- Technology Solutions:
- Examples: Virtual platforms, data analytics tools.
- Applications: Enhances remote work and decision-making.
- Transportation:
- Examples: Hybrid buses, heavy-duty trucks.
- Applications: Supports sustainable urban transit.
- Emergency Preparedness:
- Examples: Firefighting equipment, evacuation kits.
- Applications: Strengthens disaster readiness.
- Office Supplies:
- Examples: Sustainable paper products, energy-efficient devices.
- Applications: Day-to-day government operations.
Strategies for Vendors Engaging with Cooperatives
Success in cooperative purchasing demands strategic engagement. Vendors can maximize impact through the following approaches:
- Relationship Building:
- Foster connections with cooperative procurement managers.
- Attending industry and cooperative-hosted seminars.
- Contract Integration:
- Highlight cooperative contracts in sales pitches.
- Provide case studies showcasing successful cooperative engagements.
- Marketing Efforts:
- Leverage social media and newsletters for outreach.
- Host webinars for cooperative members.
- Timing Strategies:
- Register early for upcoming opportunities.
- Prepare bids ahead of contract expiration.
- Targeted Approaches:
- Analyze membership demographics for alignment.
- Focus on cooperatives that suit business offerings.
Forecast and Trends
The cooperative purchasing market is projected to reach $64.7 billion by 2025, driven by the following factors:
- Digital Transformation:
- Increased demand for IT solutions and virtual platforms.
- Service-Based Contracts:
- Growth in consulting, construction, and staff augmentation contracts.
- Post-Pandemic Recovery:
- Enhanced focus on healthcare and emergency preparedness.
Benefits and Challenges of Cooperative Purchasing
Benefits:
- Faster Procurement Cycles:
- Streamlined for emergencies.
- Cost Savings:
- Bulk purchasing reduces per-unit costs.
- Streamlined Operations:
- Lower administrative burden for governments.
Challenges:
- Policy Compliance:
- Navigating varied procurement regulations.
- Membership Complexity:
- Understanding access restrictions and cooperative structures.
Role of National vs. Regional Cooperatives
- National Cooperatives:
- Advantages:
- Broad service areas.
- Access to extensive supplier networks.
- Limitations: May overlook localized needs.
- Advantages:
- Regional Cooperatives:
- Advantages: Tailored solutions for specific industries or geographic needs.
- Limitations: Smaller contract volumes compared to national entities.
Glossary and Explanation of Industries in Cooperative Purchasing
| Architecture & Engineering: | Design and inspection for public projects. |
| Construction: | Infrastructure upgrades and road building. |
| Education Products & Services: | Textbooks and educational software. |
| Environmental Services: | GIS mapping and wildlife assessments. |
| Healthcare: | Medical supply distribution and mental health support. |
| Technology & Telecom: | IT infrastructure and wireless communication systems. |
| Public Safety: | Emergency response equipment and corrections technology. |
