State and Local Procurement Snapshot: Q3 2024
1. Executive Summary
The State, Local, and Education (SLED) market faced notable shifts in Q3 2024 as federal stimulus funding expired. Key takeaways include:
Overall Decline
A 6.0% year-over-year decline in procurement opportunities occurred as agencies grappled with tightening budgets. The education sector experienced the largest contraction at -12.9%, largely driven by the expiration of federal support, while local governments declined by -7.1%, reflecting revenue pressures at the municipal level.
Sector Resilience
Certain sectors showed resilience despite the broader downturn:
- Environmental Services:
A 4.0% increase due to sustained investment in long-term projects like waste management and water quality improvement.
- Water & Energy:
Modest growth of 1.7%, driven by renewable energy initiatives and stormwater infrastructure upgrades.
Forward-Looking Factors
The market’s trajectory remains influenced by:
- Recession concerns limiting discretionary spending.
- The upcoming presidential election is shaping federal and state priorities.
- Agencies adapt budgets to balance reduced funding and sustained service levels.
2. Market Trends and Drivers
The SLED market in Q3 2024 is navigating a complex landscape shaped by fiscal tightening, economic uncertainty, and evolving policy priorities. This section explores the primary trends and drivers influencing procurement activities across state and local governments.
Expiration of Federal Stimulus
The conclusion of the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) funding marked a pivotal shift in the fiscal landscape:
- Impact on Budgets:
Many local agencies experienced abrupt reductions in funding, leading to delayed projects and scaled-back operations.
- State-Level Preparedness:
States like California and New York proactively reallocated resources to minimize disruptions and maintain essential services.
- Municipal Challenges:
Cities and towns heavily reliant on federal aid faced significant constraints, prompting cutbacks in public services, infrastructure maintenance, and community programs.
Economic Conditions
Broader economic trends continue to shape procurement activity:
- Inflation Pressures:
Rising costs of materials, labor, and energy have forced agencies to reconsider or defer planned expenditures.
- Recession Concerns:
Uncertainty about an economic downturn has resulted in more conservative fiscal policies, especially in discretionary spending areas.
- Revenue Volatility:
Local governments reliant on property and sales tax revenues face fluctuations that complicate long-term budget planning.
Election Year Dynamics
As a presidential election approaches, policy uncertainty adds complexity to the SLED market:
- Federal Priorities:
Agencies are cautious in committing to long-term projects, awaiting potential shifts in funding priorities and regulations.
- Tax Policy Impacts:
Anticipation of tax reforms or changes in revenue allocation creates hesitancy in spending decisions.
Sector-Specific Influences
Certain sectors within the SLED market face unique challenges and opportunities:
- Education:
Declining enrollment and reduced federal support have constrained budgets, postponing investments in technology and facilities.
- Transportation:
Public transit agencies face ridership recovery challenges, leading to funding constraints and cost-saving measures like route reductions.
- Environmental Services:
Sustainability remains a focus, with investments in waste management, clean water initiatives, and renewable energy offsetting declines in other areas.
Emerging Opportunities
Despite challenges, new opportunities are emerging for vendors and contractors:
- Technology Integration:
Increased adoption of artificial intelligence and digital tools is driving demand for solutions that enhance operational efficiency and cost savings.
- Infrastructure Investments:
Federal and state-level grants continue to support large- scale projects, particularly in transportation and water management.
- Sustainability Initiatives:
Climate resilience projects are prioritizing renewable energy, energy efficiency retrofits, and green building practices.
The SLED market remains highly dynamic, with trends and drivers reflecting a blend of challenges and opportunities. Strategic adaptation and forward-looking planning will be essential for stakeholders navigating this evolving environment.
3. Sector Performance Overview
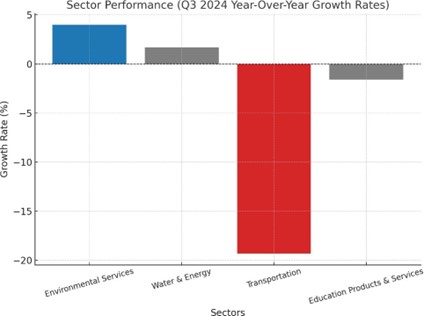
Top Performing Sectors
-
1. Environmental Services (+4.0%)
This sector’s growth stems from enduring commitments to sustainability:
★ Projects in Focus: Investments in soil conservation, wildlife restoration, and hazardous waste remediation.
★ Federal Support: Infrastructure grants contributed to project funding stability. -
2. Water & Energy (+1.7%)
Growth in this sector is attributed to:
★ Renewable Energy Projects: States like Texas and Oregon expanded solar and wind energy initiatives.
★ Stormwater Management: Coastal states prioritized flood resilience through advanced infrastructure.
Sectors Facing Challenges
-
1. Transportation (-19.3%)
Public transit systems faced operational cuts due to dwindling ridership and reduced funding. Examples include:
★ Route reductions in urban centers like Chicago and Los Angeles.
★ Delayed capital projects such as rail expansions. -
2. Education Products & Services (-1.6%)
Constrained budgets led schools to:
★  Reduce spending on new educational technologies.
★ Postpone consulting services for curriculum upgrades
4. Procurement Trends Over Time
Historical Context
Bid and RFP activity provides a window into the market’s trajectory:
- Post-Pandemic Recovery:
After the pandemic-induced decline in 2020, bid activity rebounded in 2021 and 2022, only to plateau in 2023 before declining in 2024.
- Current Volumes:
Q3 2024 saw approximately 107,000 bids, marking a 6% decrease from the same quarter in 2023.
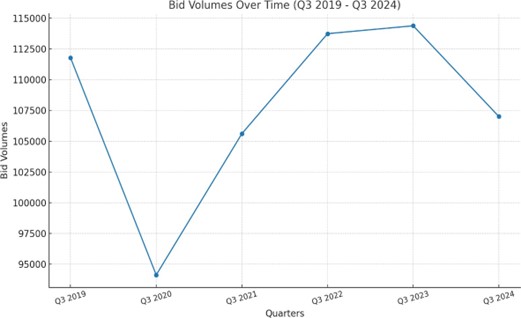
Seasonal Variability
Procurement trends exhibit distinct seasonal patterns:
- Q2 and Q4 Peaks:
These periods align with budget finalizations and year-end spending.
- Q3 Slowdown:
Traditionally a quieter period, compounded in 2024 by the withdrawal of federal funding.
5. Government Level Insights
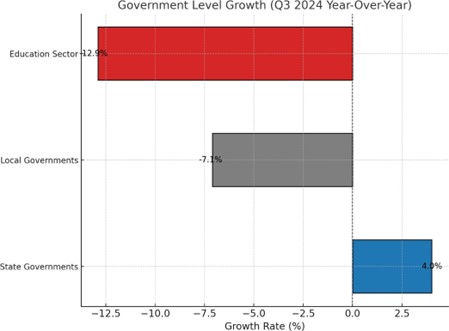
State Governments
State agencies demonstrated resilience with a 4.0% year-over-year growth:
- Infrastructure Investments:
States prioritized projects like highway expansions and broadband deployment.
- Healthcare Spending:
New contracts for public health initiatives supported growth.
Local Governments
Municipalities faced greater challenges, with a -7.1% decline:
- Revenue Shortfalls:
Reduced sales tax collections limited capital project funding.
- Service Adjustments:
Cities reevaluated public safety and transportation budgets.
Education Sector
The education sector’s -12.9% decline reflects:
- Budget Cuts:
Institutions scaled back on non-essential procurement.
- Deferred Maintenance:
Schools delayed facility upgrades due to funding gaps.
6. Technology and Innovation in Procurement
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
For this part of the report, we focused on the transformative role of artificial intelligence in state and local government procurement. Leveraging advanced analytical methods, we identified trends and keywords in bids, RFPs, and RFIs that prominently feature AI or AI-related language.
Generative AI in SLED Procurement: A New Era
Generative AI is increasingly being integrated into the SLED procurement space, appearing in bid documents as explicit requirements or suggested solutions. Examples include:
- Spend Analysis:
Using AI to categorize and analyze procurement expenditures to identify cost-saving opportunities.
- Supplier Selection:
Enhanced algorithms to evaluate and score vendor proposals based on multiple criteria.
- Demand Forecasting:
Predicting future needs for goods and services to improve inventory and resource management.
- Contract Management:
Streamlining negotiations and compliance monitoring through automated systems.
- Risk Management:
Identifying and mitigating potential risks in vendor performance and supply chain disruptions.
- Invoice Data Extraction:
Automating invoice processing to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants:
Enhancing vendor and public interactions through AI- powered conversational tools.
Support at the Highest Level
addresses, several governors highlighted AI’s potential to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making in public administration. Key examples include:
- Proactive Legislation:
Tennessee proposed legislation to regulate AI use, emphasizing transparency, ethics, and preventing misuse in public projects.
- Pilot Projects:
States like Georgia and Rhode Island launched AI-based initiatives to explore applications in procurement efficiency and workforce optimization.
Ethics and Regulation
As AI becomes more prevalent, governments are balancing innovation with caution. Transparency and ethical guidelines are at the forefront of AI-related legislation, ensuring that the technology aligns with public interest and operational integrity. Efforts to standardize disclosures of AI use in bids are gaining traction, fostering trust and accountability in the procurement process.
Looking Ahead
The integration of AI in procurement is set to accelerate, with its applications extending into areas such as predictive analytics and digital transformation. Vendors and contractors are advised to align their offerings with this trend, emphasizing AI-enabled solutions that drive efficiency and sustainability in government operations.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI continues to transform procurement processes:
- Efficiency Gains:
Applications include demand forecasting, supplier evaluations, and compliance checks.
- State Leadership:
States like Georgia piloted AI tools to streamline procurement operations.
Emerging Developments
AI adoption also includes:
- Transparency Regulations:
Efforts to ensure ethical use of AI in decision-making.
- Cross-Agency Collaboration:
Shared AI platforms enabling more cohesive procurement strategies.
7. Industry Glossary
Key Industries
- Environmental Services:
Encompasses environmental testing, soil conservation, and waste management.
- Water & Energy:
Focused on utility upgrades, renewable energy, and water treatment systems.
- Technology & Telecom:
Includes IT infrastructure, cloud services, and telecommunications.
- Healthcare:
Covers medical supplies, public health programs, and social services.
- Transportation:
Encompasses transit systems, logistics planning, and infrastructure consulting.
8. Conclusion
The Q3 2024 SLED Procurement Snapshot reflects a market in transition. While many sectors grapple with reduced budgets, opportunities remain in areas like Environmental Services and Water & Energy. Adopting innovative solutions, such as AI, and strategically aligning priorities will be crucial for stakeholders navigating the evolving landscape of state and local government procurement.
